Electrics & electronics
The Electrical & Electronics category includes pick-and-place machines, complete assembly lines, PCB manufacturing equipment, energy systems, studio equipment, and IT systems. It also covers drives, motors, and measurement and control technology. The offered used machines are suitable for various industrial applications and are available at competitive auction prices.
181 Positions
Refresh in 15s

Auction
#18242-486
Heat exchanger FRIMEC VROL Typ 18
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 501, Außenbereich Container/ EPSL
17. Mar 2026, 11:14 AM
2.600 €
1 Bids (Subject to Reservation)
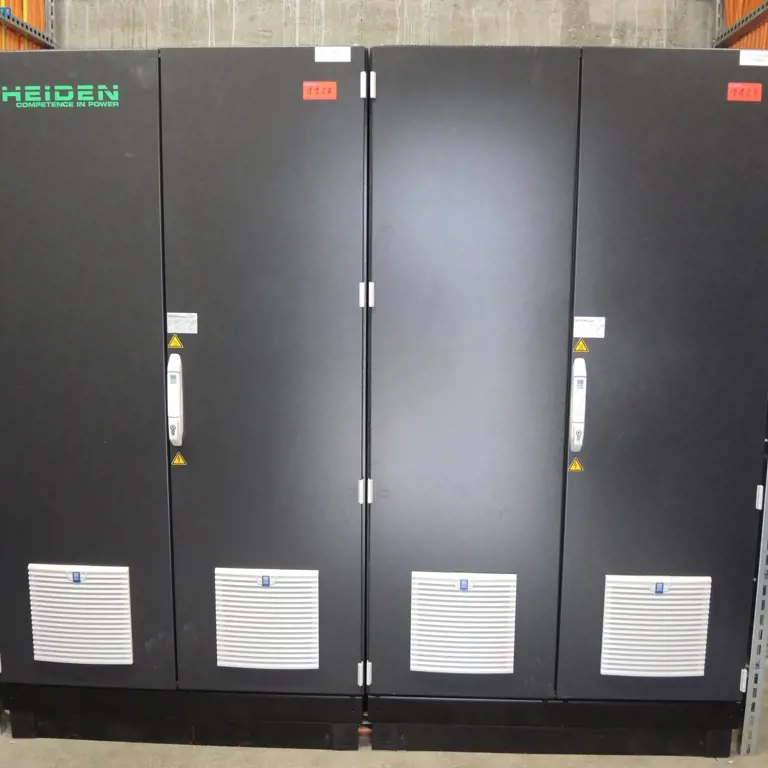

Auction
#18242-1128
Direct current supply / DC power supply 650 kW HeidenPower
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 342, Gebäude 342, EG/ Nebenraum Stromversorgung
17. Mar 2026, 11:15 AM
70.000 €
1 Bids (Subject to Reservation)

Trading
#19339-205
Switch cabinet
Anton-Böhlen-Straße 26, 34414 Warburg
18. Mar 2026, 10:00 AM
5 €
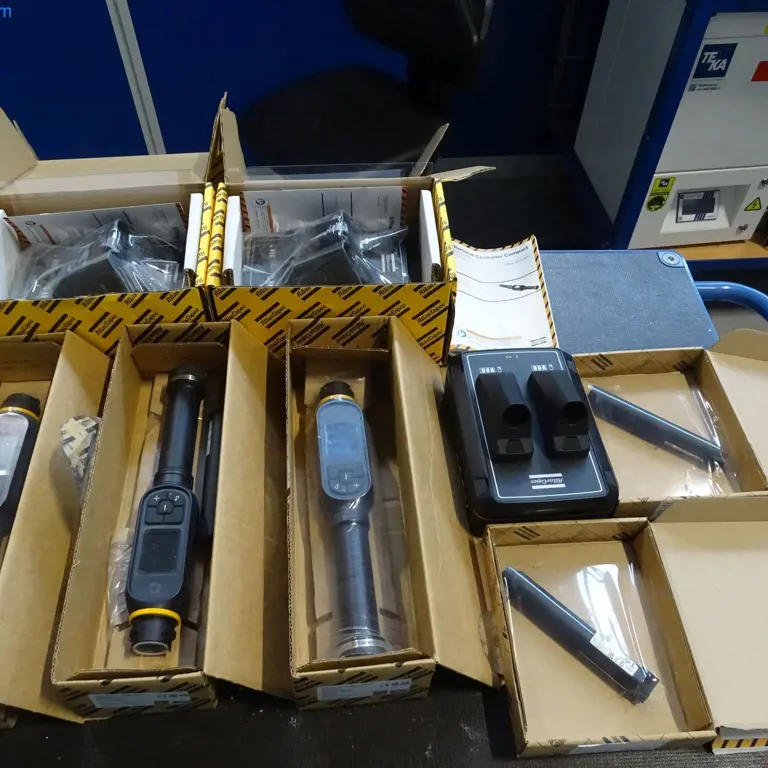

Auction
#18242-93
3 Intelligent torque wrench Atlas Copco STRwrench Controller Compact
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 502, Halle 502, EG, Central Tool Store/ Werkzeugausgabe
26. Mar 2026, 10:00 AM
2.000 €

Auction
#18242-118/1
Gleichstrom-Versorgung / DC Power Supply 650 kW (already dismantled) HeidenPower
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 342, Gebäude 342, EG
26. Mar 2026, 10:02 AM
70.000 €

Auction
#18242-122/1
3 load cells ME-Systeme K6D80 5 kN 250 Nm MP11
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 342, Halle 342, EG
26. Mar 2026, 10:02 AM
900 €

Auction
#18242-123/1
AC Power Supply 650 kW (stored dismantled)
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 502, Halle 502, EG/ Propulsion / Triebwerktest
26. Mar 2026, 10:03 AM
2.000 €
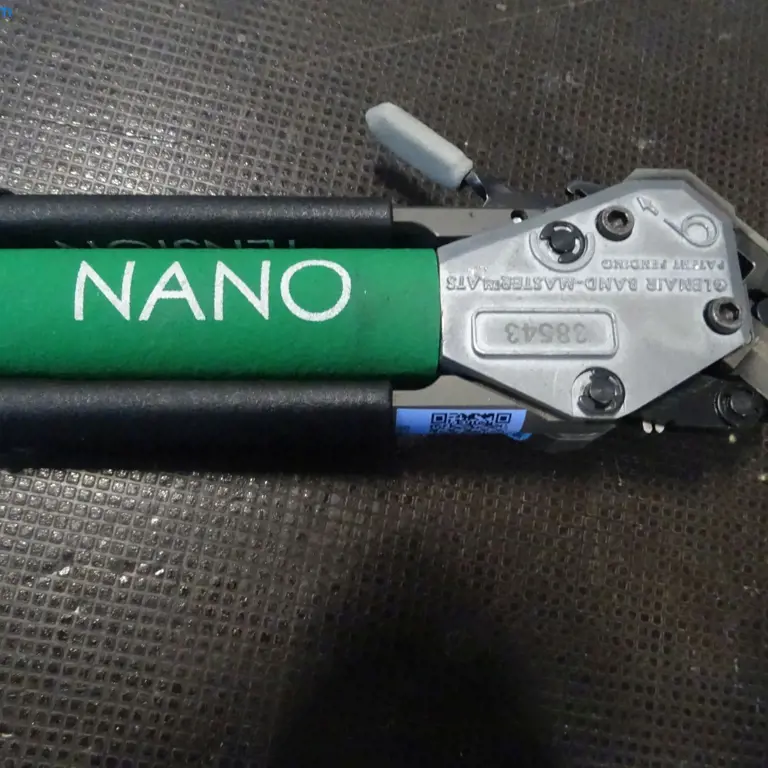
Auction
#18242-153/7
Nano banding tool (HT00204-001) Glenair Band-Master
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 502, Halle 502, EG/ Halle Endmontage FAL
26. Mar 2026, 10:04 AM
250 €

Auction
#18242-153/8
Nano banding tool (HT00204-002) Glenair Band-Master
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 502, Halle 502, EG/ Halle Endmontage FAL
26. Mar 2026, 10:04 AM
250 €

Auction
#18242-153/9
Nano banding tool (HT00204-003) Glenair Band-Master
82131 Gauting, Galileostr. 502, Halle 502, EG/ Halle Endmontage FAL
26. Mar 2026, 10:05 AM
250 €
Buy used electric machines on NetBid
There are different types of electric machines, which are used for different purposes and differ in the way they work. With us, you will find a wide range of cost-effective items for your needs.
What are electric machines?
An electric machine is designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy or vice versa. It is required for a variety of applications, such as Driving machines and equipment, generating electricity, controlling speeds and torque, pumps and compressors, moving and storing workpieces and materials, etc.
There are many different types of electric machines, some of the most important are:
Direct current machines (DC machines)
Direct current machines (DC machines) convert electrical energy into mechanical energy or vice versa. They are often used in applications where continuous rotary motion is required, such as electric trains, electric cars and electric tools. They are also used in industrial processes to control valves and pumps.
Alternating current machines (AC machines)
Alternating current machines (AC machines) convert electrical energy into mechanical energy or vice versa. They are used for a variety of applications, such as power tools, fans, compressors and electric motors for large industrial plants. One of their advantages over DC machines is that they can be easily transported over long distances without losing power.
Synchronous machines
Synchronous machines are a type of AC machine in which the speed of rotation is constant and matches the frequency of the applied AC current. They are often used as generators in power plants to produce electrical energy. They are also used as drives in some applications where high efficiency and precise speed control is required, such as turbines and pumps.
Asynchronous machines
Asynchronous machines, also known as induction machines, are a type of alternating current machine where the speed of rotation is slightly different from the frequency of the applied alternating current. They are often used in applications where efficient and cost-effective transmission of electrical energy is required, such as in household appliances, power tools and industrial equipment. They are also used to drive fans, compressors and electric motors.
Stepper motors
Stepper motors are electromechanical devices that operate in steps and enable precise positioning. They are used when precise motion control is required, such as in 3D printers, CNC machines, moving platforms and other applications.
Servo motors
Servo motors are electric drives that enable precise positioning and speed control. They contain an actuator and feedback to monitor and, if necessary, adjust the position of the rotor. Servo motors are designed for applications where high precision and speed control is required, such as in robots, CNC machines, moving platforms and industrial processes.
Generators
Generators are devices that produce electrical energy by converting mechanical energy. They work on the basis of the electromagnetic law of induction, in which a moving conductor generates electrical voltage in a magnetic field. Generators are often used in power stations to produce electrical energy which is then fed into the power grid. They are also necessary for emergency power generators, ships and airplanes to ensure the power supply when no external power source is available.
Each type of electric machine has its own special characteristics and is optimized for specific applications.









